Overview
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) uses a pair of custom primers to direct DNA elongation toward each other at opposite ends of the sequence being amplified. These primers are typically between 18 and 24 bases in length and must code for only the specific upstream and downstream sites of the sequence being amplified. A primer that can bind to multiple regions along the DNA will amplify them all, eliminating the purpose of PCR.
A few criteria must be brought into consideration when designing a pair of PCR primers. Pairs of primers should have similar melting temperatures since annealing during PCR occurs for both strands simultaneously, and this shared melting temperature must not be either too much higher or lower than the reaction's annealing temperature. A primer with a Tm (melting temperature) too much higher than the reaction's annealing temperature may mishybridize and extend at an incorrect location along the DNA sequence. A Tm significantly lower than the annealing temperature may fail to anneal and extend at all.
Additionally, primer sequences need to be chosen to uniquely select for a region of DNA, avoiding the possibility of hybridization to a similar sequence nearby.
Also, there are other parameters to be taken in account - Gibbs free energy, self- and heterodimers availability, etc. All parameters are described below in details.
UGENE provides the "PCR Primer Design for DNA Assembly" feature only for nucleic sequences with the "Standard DNA" alphabet. To use it in UGENE open a DNA sequence and go to the "PCR Primer Design for DNA Assembly" tab of the Options Panel:
There are the following parameters:
Forward primer - forward primer.
Reverse primer - on the opposite strand from the forward primer.
Mismatches - mismatches limit.
3' perfect match - specify the number of nucleotides at the 3' end that must not have mismatches.
Maximum product - maximum size of the amplified sequence.
Extract annotations - specify the type of extracted annotations: Inner, All intersected or None.
- Value Inner is selected by default. When this value is selected, the extracted PCR product contains annotations from the original sequence, located within the extracted region.
- Value All intersected specifies that all annotations of the original sequence that intersect the extracted region must be extracted as well.
- Value None specifies that annotations from the original sequence must not be extracted.
Choosing primers
Type two primers for running In Silico PCR. If the primers pair is invalid for running the PCR process then the warning is shown. Also, primers for the running In silico PCR can be chosen from a primer library. Click the following button to choose a primer from the primers library:
The following dialog will appear:
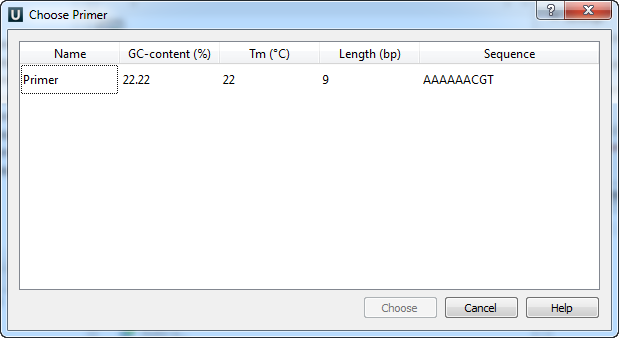
The table consists of the following columns: name, GC-content (%), Tm, Length (bp) and sequence. Select primer in the table and click the Choose button.
Click the Reverse-complement button for making a primer sequence reverse-complement:
Click Show primers details for seeing statistic details about primers.
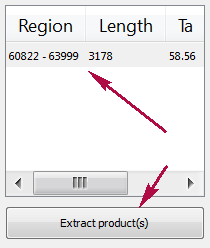
When you run the process, the predicted PCR products appear in the products table.
Products table
There are three columns in the table:
- region of product in the sequence
- product length
- preferred annealing temperature
Click the product for navigating to its region in the sequence.
Click the Extract product(s) button for exporting a product(s) in a file or use double click for that.