The Remote BLAST plugin provides the capability to annotate sequences with information stored in remote databases.
To perform a remote database search open the Sequence View, select the sequence region to analyze and click the Analyze ‣ Query remote database context menu item. If a region is not selected the whole sequence will be analyzed.
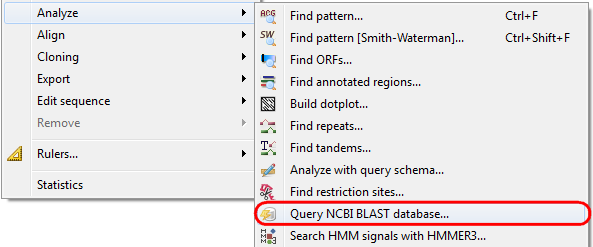
The following dialog will appear where you can choose the search options:
General options are:
Select the search type — in the remote databases the blastn search is used for nucleotide sequences, blastp and cdd searches are used for amino sequences.
UGENE also provides a way to use blastp and cdd searches for nucleotide sequences. This is achieved by translating the nucleotide sequence into the amino sequences.
When a sequence is translated the translation table from the active Sequence View is used. Finally, all 6 translations are used to query the remote database with the selected blastp or cdd search.
Expectation value — this option specifies the statistical significance threshold for reporting matches against database sequences. Lower expect thresholds are more stringent, leading to fewer chance matches being reported.
Max hits — the maximum number of hits that will be shown (not equal to number of annotations).
Database — the target database.
Search for short, nearly exact matches — automatically adjusts the word size and other parameters to improve results for short queries.
Megablast — select this option to compare query with closely related sequences. It works best if the target percent identity is 95% or more, but it is very fast.
You can see the description of the annotation saving parameters here.
Search timeout — sometimes a database doesn’t respond, therefore you need to re-wait for the response. This option sets the time that will be spent for re-appeal to the database. Note that in case of long sequences time for request preparation increases and the search takes several minutes.
Also there is Advanced options tab:
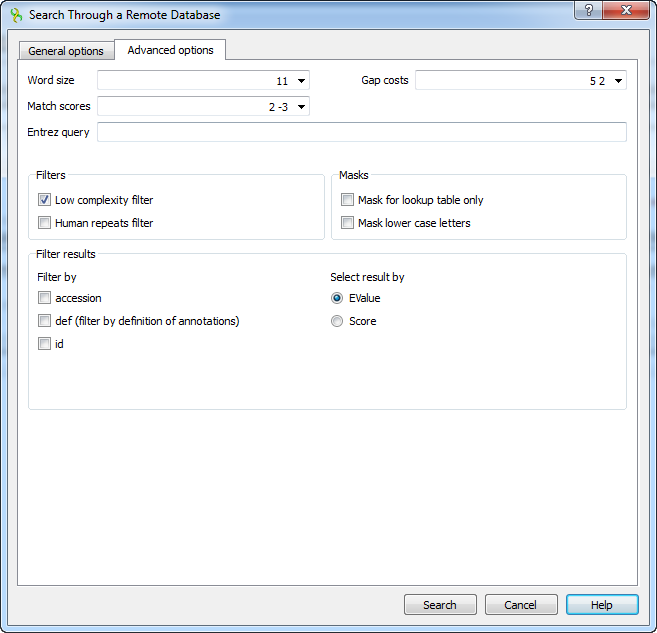
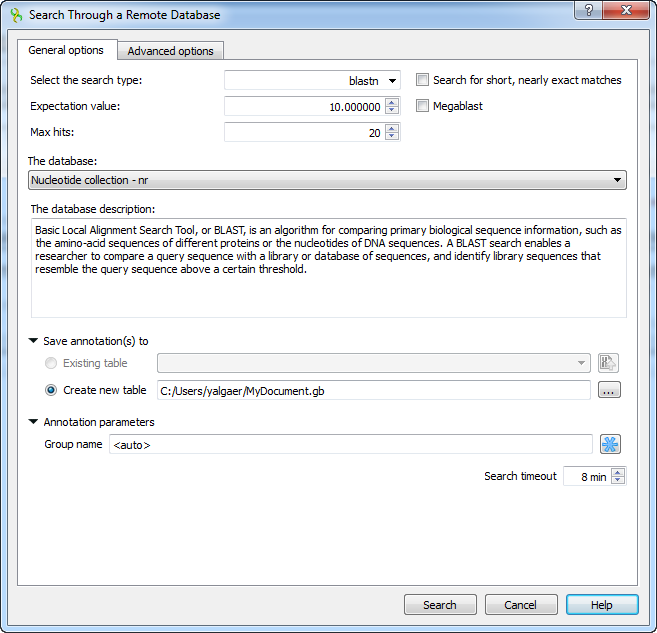
The view of the Advanced options tab depends on the selected search. For the blastn search it looks like on the picture above.
Word size — the size of the subsequence parameter for the initiated search.
Gap costs — costs to create and extend a gap in an alignment. Increasing the Gap costs will result in alignments which decrease the number of Gaps introduced.
Match scores — reward and penalty for matching and mismatching bases.
Entrez query — a BLAST search can be limited to the result of an Entrez query against the database chosen. This restricts the search to a subset of entries from that database fitting the requirement of the Entrez query. Examples are given below:
protease NOT hiv1[organism] — this will limit a BLAST search to all proteases, except those in HIV 1.
1000:2000[slen] — this limits the search to entries with lengths between 1000 to 2000 bases for nucleotide entries, or 1000 to 2000 residues for protein entries.
Mus musculus[organism] AND biomol_mrna[properties] — this limits the search to mouse mRNA entries in the database. For common organisms, one can also select from the pulldown menu.
10000:100000[mlwt] — this is yet another example usage, which limits the search to protein sequences with calculated molecular weight between 10 kD to 100 kD.
src specimen voucher[properties] — this limits the search to entries that are annotated with a /specimen_voucher qualifier on the source feature.
all[filter] NOT enviromnental sample[filter] NOT metagenomes[orgn] — this excludes sequences from metagenome studies and uncultured sequences from anonymous environmental sample studies.
For help in constructing Entrez queries see the Entrez Help document.
Filters — filters for regions of low compositional complexity and repeat elements of the human’s genome.
Masks for lookup table only — this option masks only for purposes of constructing the lookup table used by BLAST so that no hits are found based upon low-complexity sequence or repeats (if repeat filter is checked).
Mask lower case letters — with this option selected you can cut and paste a FASTA sequence in upper case characters and denote areas you would like filtered with lower case.
Filter by — filters results by accession, by definition of annotations or by id.
Select result by — selects results by EValue or by score.
When the blastp search is selected in the general options, the view of the Advanced options tab is the following:
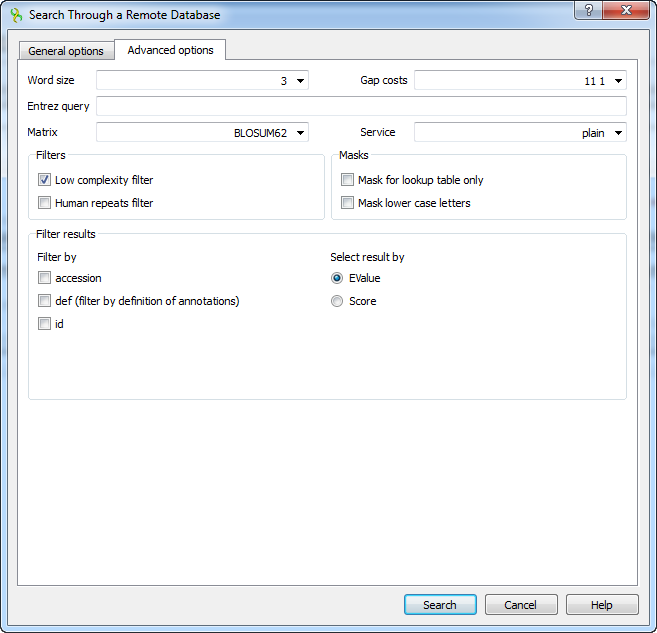
As you can see there is no Match scores option, but there are Matrix and Service options.
Matrix — key element in evaluating the quality of a pair-wise sequence alignment is the “substitution matrix”, which assigns a score for aligning any possible pair of residues.
Service — blastp service which needs to be performed: plain, psi or phi.
The Advanced options tab is not available when the cdd search is selected.